1、 Preface.
1. Introduction to Import and Export Trade.
Import and export trade consists of import trade and export trade, that is, cross-border trade in goods and services. It plays an important role in adjusting the utilization rate of domestic production factors, improving the international supply and demand relationship, adjusting the economic structure, and increasing fiscal revenue.
According to the content of trade, import and export trade can be mainly divided into processing trade, general trade, and service trade. Among them, processing trade refers to the business activities of enterprises that import materials (parts, components, raw and auxiliary materials, etc.) and then re export their finished products after processing or assembly ¹。 General trade refers to a trade method opposite to processing trade, which refers to the unilateral import and export trade method of importing/exporting customs territory. The transaction goods are the normal trade import and export goods sold by enterprises unilaterally. Service trade refers to the trade behavior in which a legal person or natural person of a country provides services to a foreign legal person or natural person, including commercial services, communication services, construction engineering services, financial services, etc. The proportion of the three in a country's total import and export trade can directly reflect the current situation of the country's import and export trade.
2. Domestic and foreign trade situation.
Since the outbreak of the COVID-19 in 2020, the economies of countries around the world have suffered from different degrees of impact. International import and export trade once fell into a state of substantial stagnation, and trade protectionist measures have increased significantly. In 2021, with the adjustment of epidemic prevention policies in many countries, the world's import and export trade experienced a certain degree of recovery under the situation of continuous fluctuations in the epidemic. However, it is also facing a series of challenges such as rising commodity prices, global energy supply shortages, and sharply increasing pressure on the industrial chain supply chain. From the beginning of 2022 to the present, the world political situation has been turbulent, the conflict between Ukraine and Russia has continued to ferment, the energy crisis in Europe has become prominent, and developed countries such as Europe and the United States have accelerated the tightening of macroeconomic policies, which has to some extent affected the global economic pattern, making the trend of world import and export trade even more uncertain.
In the early stage of the outbreak of the epidemic, production and living in some regions of China were greatly affected. However, with the rapid and effective implementation of the government's epidemic prevention policies, China became the first major economy in the world to resume growth since the outbreak of the epidemic, driving the orderly recovery of domestic import and export trade to some extent. Since 2021, China's economy has continued to recover steadily, production has steadily increased, and market expectations have improved, providing a good economic environment for import and export trade. In addition, China actively promotes reform and innovation in trade facilitation, accelerates the construction of characteristic service export bases in fields such as culture and digital services, expands the scope and autonomy of pilot zones such as free trade zones and free trade ports, builds a global network of high standard free trade zones, and supports the development of import and export trade with high-level openness ²。
2、 Current situation analysis.
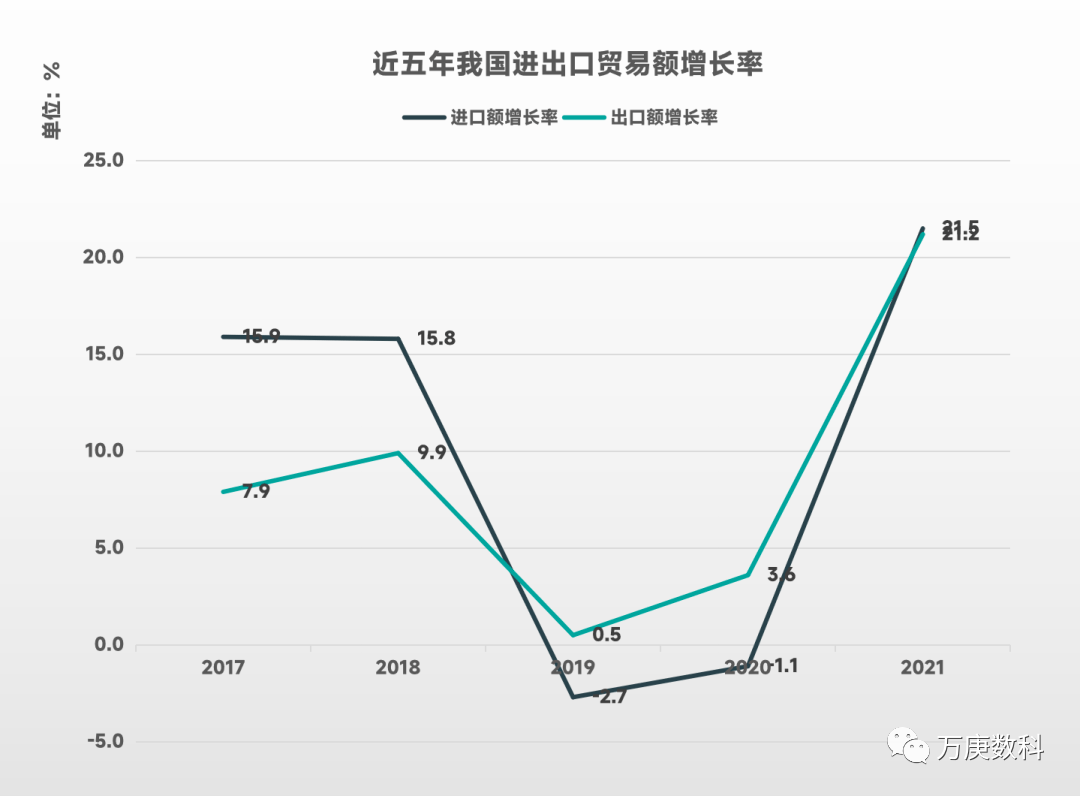
1. China's import and export volume and its growth rate.
(Data source: General Administration of Customs)
During 2017-2021, China's total import and export trade maintained an overall growth trend. Among them, in 2019, the growth rate of import and export volume both decreased significantly, and in 2020, the growth rate slightly rebounded, and rapidly climbed in 2021. Both growth rates reached over 21%.
The reason for this is that in 2019, the global economic growth slowed down, unilateralism and protectionism rose, trade frictions between Europe, the United States and China frequently occurred, and the international import and export trade situation was severe and complex. Although the domestic economy has maintained a stable operation, and the government has continued to expand openness and improve the quality of import and export trade, the impact of the international trade situation still led to a significant decline in the growth of China's import and export trade that year. In 2020, the COVID-19 broke out, and the economies of various countries experienced different degrees of recession. Although China controlled the epidemic and resumed production at a relatively fast pace, the shrinkage of the international consumer market still brought great restrictions on the growth of China's import and export trade. In 2021, the adjustment of epidemic prevention policies by major economies in the world, coupled with the accelerated recovery of the world economy, led to a rapid growth in China's import and export volume. This shows that China's import and export trade volume is greatly affected by the world economic situation, with strong cyclical volatility.
In addition, from the perspective of the scale of China's import and export trade volume in the past five years, China's export trade volume is both larger than the import trade volume, and the gap is expanding. This indicates that China's foreign trade status belongs to a trade surplus, which on the one hand reflects that China is in a relatively favorable position in foreign trade, and on the other hand reflects that China's economic growth is increasingly dependent on external demand.
2. Total international import and export trade.
(Data source: WTO)
In the past five years, the total amount of international import and export trade has shown a trend of "up down up", and the overall trend remains upward. However, it is worth noting that in 2020, the volume of international import and export trade decreased to the level before 2017, which is slightly higher than the change in China's import and export trade volume in that year. This shows that China's import and export trade has a relatively strong resilience, and in the face of factors such as uneven development and policy diversity among participating countries in international trade, it is easier to maintain a relatively stable import absorption and export output capacity, achieving a long-term stable growth trend.
3. The proportion of China's import and export volume in the total international import and export volume.
(Data source: General Administration of Customs, WTO)
Since 2018, the proportion of China's import and export trade in the total international volume has continued to rise. This shows that China has an important driving role in the development of international import and export trade, and its position and voice in international trade are constantly increasing. In addition, in 2020, China's export trade volume accounted for a significant increase in the proportion of total international trade, indicating that China's epidemic prevention and control policies, as well as policies and measures to stabilize foreign trade, have taken effect, the market share of international trade has increased against the trend, and the business environment of foreign trade enterprises continues to improve, helping to stimulate the vitality of market entities.
4. Proportion of China's import and export trade countries/regions.
(Data source: General Administration of Customs)
According to the proportion of China's import trade countries/regions in the first half of 2022, the main sources are ASEAN, the European Union, Taiwan, China, and South Korea, Japan, the United States, and Australia are also important components. From the perspective of the proportion of countries/regions in export trade, the United States, the European Union, and ASEAN are the main targets of China's export trade, while Hong Kong, Japan, and South Korea are also important components.
It is not difficult to find that the United States, the European Union, ASEAN, Japan, and South Korea all account for an important share in China's import and export trade. This indicates that China's current foreign trade trading market has a certain degree of concentration, and there are signs of regional imbalances. However, it cannot be ignored that as China's import and export trade volume gradually increases in the proportion of global trade, more and more countries and markets will become China's new important foreign trade trading targets. For example, in the first half of the year, China's export growth to India, Brazil, Australia and other economies reached more than 20%, and the export growth to countries along the "the Belt and Road" reached 17.8%. It indicates that China's import and export trade market will be more diversified in the future.
5. China's import and export product structure.
(Data source: General Administration of Customs)
From the perspective of China's product import structure in the first half of 2022, mechanical and electrical products reached the highest level, with 39.1%; Followed by high-tech products, accounting for 28.4%; Then came crude oil, agricultural products, and iron ore, with 13.4%, 8.5%, and 5.1%, respectively. This indicates that China has a large external demand for technological products, and also relies to a certain extent on the import of energy, grain, and industrial raw materials.
From the perspective of China's product export structure in the first half of 2022, mechanical and electrical products are still the highest, but the proportion has reached 55.4%; The second is high-tech products, slightly lower than the proportion of imports, at 25%; Clothing, textile yarn, and steel accounted for 5.5%, 4.1%, and 3.5%, respectively. This indicates that China's export products are mainly industrial products, but the proportion of high-tech products is not high, and the export trade structure needs to be further optimized.
6. Composition of import and export trade modes.
(Data source: General Administration of Customs)
Since 2018, the proportion of China's general trade in import and export trade has steadily increased, from 56% to 64%; The proportion of processing trade continued to decline, from 32% to 20%; The proportion of other trade (mainly service trade) has increased overall, but has declined slightly this year. This indicates that processing trade with low added value is accelerating its transformation into general trade and service trade. China's import and export trade patterns continue to be optimized, but the proportion of service trade needs to be further improved.
7. Top 10 provinces with import and export trade volume.
(Data source: General Administration of Customs)
From the perspective of the top ten provinces in China's import and export trade volume last year, there are the following characteristics: First, the overall situation is in a "one super and multiple strong" situation, with Guangdong Province leading the way with a proportion of over 21%. Although there is a large gap between Jiangsu, Zhejiang, and Shandong and Guangdong, they also have a certain weight; The second is that coastal provinces have an absolute advantage in the proportion of import and export trade, with the top five coastal provinces accounting for nearly 60% of the total. This is mainly due to various factors such as geographical advantages, historical foreign trade policies, and so on; Third, the inland provinces in the central and western regions also have great growth potential. With the continuous implementation of the "the Belt and Road Initiative" and the expansion of the pilot of the inland free trade zone, the scale of import and export trade in the central and western inland regions is expected to grow rapidly and become an important part of China's import and export trade in the future.
3、 Future outlook.
1. The volume of import and export trade has steadily increased, playing a more important role in international trade.
On the one hand, China's import and export trade volume has reached new highs in recent years, and the scale of trade in goods has continuously jumped. In 2018, the import and export volume of goods trade exceeded the 30 trillion yuan mark, and in 2021, it was close to the 40 trillion yuan mark. The international market share increased from 10.4% in 2012 to 13.5% in 2021. Since 2017, China has maintained its position as the world's largest country in import and export trade for five consecutive years.
On the other hand, compared to developed countries, China has entered the WTO relatively late, has not participated in international import and export trade for a long time, and has failed to have a voice that matches the national strength in the formulation of international trade rules. As China's economic and trade cooperation with major economies deepens, and its position as the largest country in import and export trade continues to stabilize, China will also have more voice in international trade, and gradually realize the transformation from a participant and rule follower to a leader and rule setter in international trade.
2. The import and export structure has been continuously optimized, and service and technology exports have driven new growth points.
Since the reform and opening up, China has long been in a state of unbalanced import and export of imported technical products and exported processed products. In recent years, with the transformation and upgrading from "Made in China" to "Made in China", the leading industries in China's export structure have transformed and upgraded from traditional labor intensive products to high-tech industries. The quality, grade, and added value of export products have continuously improved. The rapid growth of exports of technical products and services has brought new growth points for foreign trade. It also makes China stronger in participating in the competition of international import and export trade, playing a greater role in the economic engine, and laying a stronger foundation for long-term development ³。
3. Diversified import and export trade targets and deepened economic and trade cooperation with more economies.
As China's participation in international import and export trade continues to expand in depth and breadth, the "circle of friends" of foreign trade also continues to expand. In recent years, China's trade with countries along the "the Belt and Road" has continued to deepen and smooth, and has comprehensively deepened international cooperation with customs. Through the cooperation initiative of "smart customs, smart borders, and smart sharing connectivity", China has established friendly cooperative relations with customs in 171 countries and regions, and deeply participated in the World Trade Organization (WTO) The World Customs Organization (WCO) and the negotiation of free trade agreements such as the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (RCEP) have not only promoted the diversification of China's import and export trade targets, but also created a good external environment for domestic foreign trade enterprises.
4. Coastal provinces will continue to dominate for a long time, with great growth potential in central and western provinces.
Due to the good import and export trade foundation of coastal provinces and their natural advantageous geographical advantages, in the long run, China's import and export trade share will still be dominated by coastal provinces. However, with the accelerated layout of pilot free trade zones in the central and western regions, and the development of emerging trade forms such as service trade and technology trade, the proportion of imports and exports in the central and western regions of China has increased from 11.1% a decade ago to 17.7% last year. In the future, it is expected that the import and export trade volume in the central and western regions will still maintain rapid growth, driving China's total import and export trade to usher in a new round of breakthroughs.